Inspection of Diesel Engine Turbocharger Blades
Diesel engine turbocharger blades have complex shapes that cannot be measured by conventional means such as calipers. If the number is not large, it can be detected with CMM; it can also be used for 3D scanning. However, 3D scanning is often used in reverse engineering, and its cost, efficiency, and accuracy are not enough to support the quality inspection requirements of conventional mass-produced products.
Therefore, the development of a fast, accurate and low-cost blade airfoil shape inspection tool has become the responsibility of every blade manufacturer. We have produced diesel engine turbocharger blades for diesel locomotives in Russia and the CIS countries. The inspection of these blades has brought great challenges to our quality department. These challenges have been developed after we have developed inspection tools. Solved. In the follow-up inspection, each inspector can inspect at least 300 pieces per day, and the defective product rate can be controlled within one thousandth. Our excellent quality control has won the trust of our customers. Below I will show you our inspection tooling:
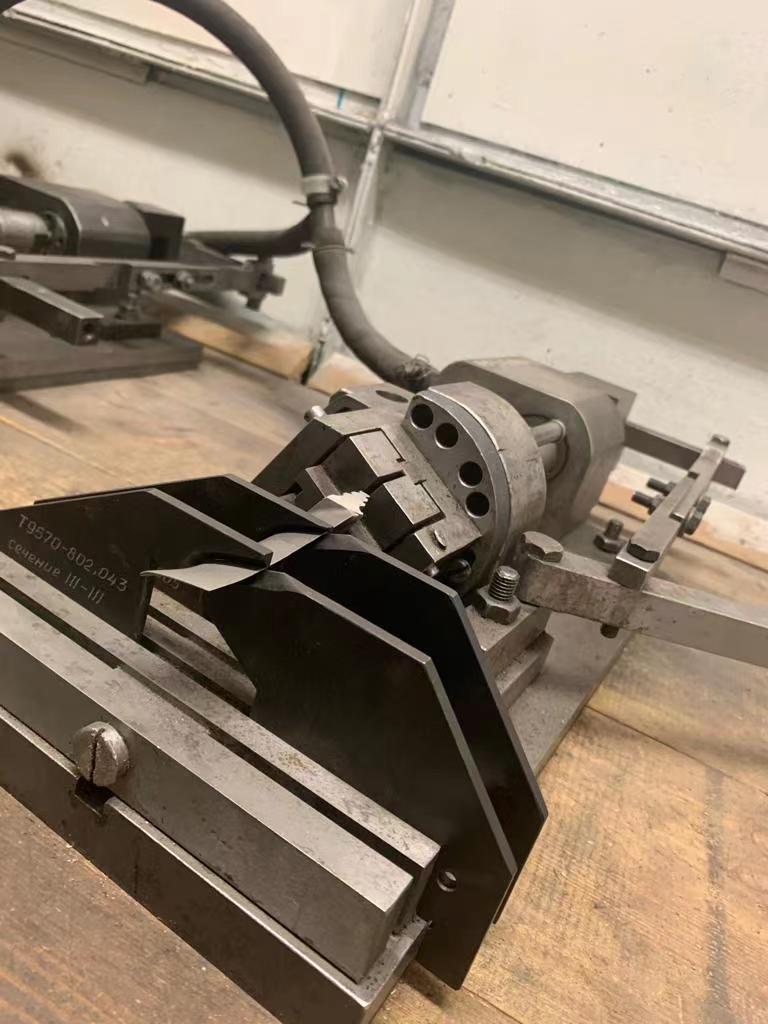

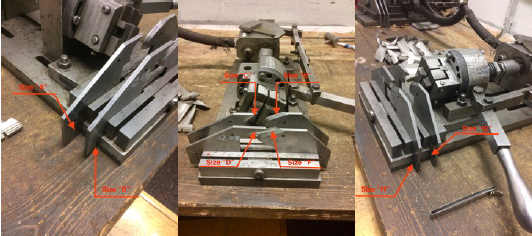
The inspection tooling mainly consists of three parts:
1. The cylinder part is used to push the collet to clamp the BASE(Fir-Tree)
2. BASE(Fir-Tree) chuck, the shape of which is consistent with the BASE(Fir-Tree) of the blade
3. The plates, whose shape is consistent with the profile of the blade
The inspection tool is connected to the air pump, and there is a manual switch to control the opening and closing of the tool. After the blade is put on, use a flashlight to visually check the 4 points of each pair of plates. If there is a gap, use a feeler gauge to measure the size of the gap to determine whether the deformation of the blade is within an acceptable range.
Different blades have different α angles, and four types of blades can be measured by switching between four pin holes.
In addition to the airfoil shape detection, the detection of BASE(Fir-Tree) is also essential. BASE(Fir-Tree) detection is to measure with a common normal micrometer and a pin gauge.
In addition, COLOR DEFECTS TEST-LUMINA TEST is used to detect cracks on the blade surface, and X-ray inspection is used to view casting defects inside the blade. Various inspection methods cooperate with each other to ensure that every blade we provide to customers is qualified.